Subtotal: 0,00 MT
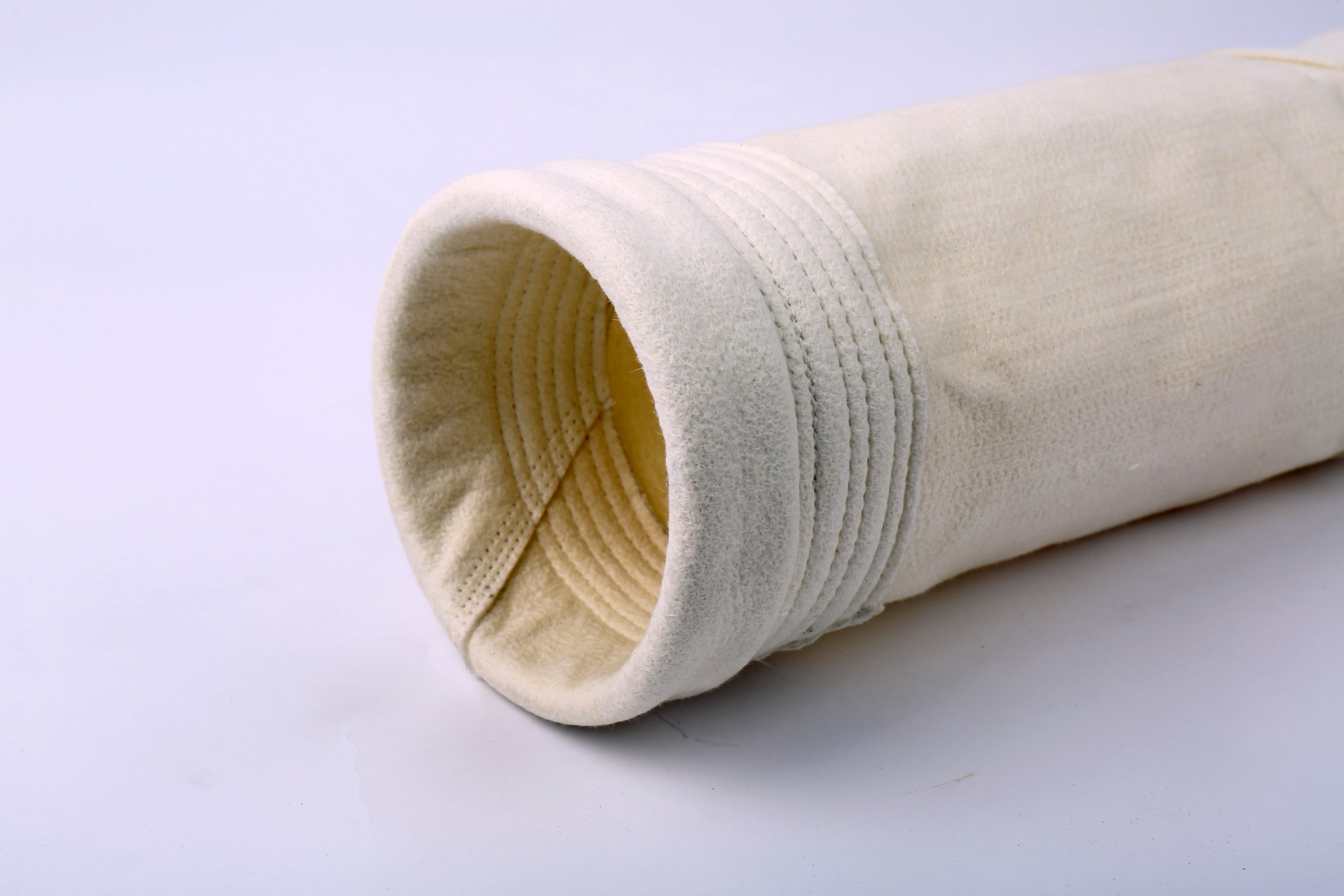
Fiberglass Filter Bag
Fiberglass needle filter bags are a staple in high-temperature industrial filtration, prized for their ability to withstand extreme heat and their robust structure.
Description
Fiberglass filter bags are a staple in high-temperature industrial filtration, prized for their ability to withstand extreme heat and their robust structure.
Here’s a breakdown of their key characteristics and applications:
Manufacturing and Properties:
- Material: These bags are made from fiberglass fibers, which are known for their inherent heat resistance. These fibers are then processed into a needle felt fabric.
- Needle Punching: The fiberglass fibers are mechanically interlaced through the needle-punching process, creating a porous and strong filtration medium.
- Key Properties:
- High-Temperature Resistance: Fiberglass filter bags can withstand continuous operating temperatures of up to approximately 260°C (500°F), and can handle short-term temperature spikes even higher.
- Dimensional Stability: They maintain their shape and size under high temperatures, ensuring consistent filtration performance.
- Chemical Resistance: Fiberglass offers good resistance to many chemicals, but its resistance to strong alkalis is limited.
- Durability: They are known for their strength and resistance to tearing.
- Construction: The fiberglass felt is fabricated into filter bags with various configurations and surface treatments to fit into filtration systems. Surface treatments can include PTFE coatings or other chemical coatings to enhance particulate release or to improve resistance to certain chemicals.
Applications:
- Cement Industry: Filtering dust from kiln exhaust and other high-temperature processes.
- Power Plants: Used for filtering fly ash from boiler exhaust.
- Metallurgical Industry: Filtering fumes and dust from metal processing.
- Asphalt Plants: Filtering of hot gases from asphalt production.
- Waste Incineration: Filtration of high-temperature gases produced during waste incineration.
Advantages:
- Exceptional High-Temperature Resistance: Provides reliable filtration in extremely hot environments.
- Good Dimensional Stability: Maintains its shape and performance under high heat.
- Good chemical resistance: Resistant to many acids.
- Relatively cost-effective: When compared to some of the higher-end temperature filter media, such as PTFE.
Important Considerations:
- Alkali Sensitivity: Fiberglass is vulnerable to degradation by strong alkalis, so its use in such environments is limited.
- Fiber Breakage: Fiberglass can be subject to fiber breakage, especially when subjected to excessive physical strain.
Finish Treatment:
- Antistatic Line Type (AS–L).
- Antistatic Blend Type (AS–B).
- Antistatic Cross Line Type (AS-X).
- PTFE Membrane (M).
- PTFE impregnation (TPI).
- Water & Oil Repellent (WR).

 Aramid Filter Bag
Aramid Filter Bag